
Pneumatic retinopexy: This procedure is used for a small tear in the retina.Cryopexy involves freezing the layers of the eye - including the retina - by placing a very cold metal probe against its wall, resulting in an adhesive scar that seals the retina. Laser (photocoagulation) or freezing (cryopexy): Photocoagulation is a laser treatment where the laser shine makes small burns around the retina tear or hole, and these small burn scars fix the tear.While retina transplant for the treatment of inherited retinal diseases has been widely researched about, retinal detachment can be treated with one or more of these procedures: Severe eye injury, or past injuries that haven’t been treatedĪ detached retina won’t heal on its own and medical attention is necessary.
 Eye disease or disorder like retinoschisis, uveitis or thinning of the peripheral retina (lattice degeneration). Ageing - people over the age of 50 have a higher risk of developing it. Risk-increasing Factors of Retinal Detachmentīelow are factors that increase the risk of developing a retinal detachment: Conditions such as injury, inflammatory disorders, tumours or age-related macular degeneration are the common causes of Exudative Detachment. Exudative: This type of detachment happens when fluid builds up behind the retina, but there is no retina damage - no holes or tears in the retina. People with poorly controlled diabetes or other conditions may be at risk or experience Tractional Detachment. Tractional: This type of detachment occurs when the retina pulls away from the back of the eye because of scar tissue growing on the retina’s surface. Rhegmatogenous is largely associated with ageing, but one can also have it due to an eye injury or severe nearsightedness. Also, if the vitreous - which is the gel-like material in the inside of your eye - passes through the tear to the space behind the retina, it might result in retinal detachment. The tear also allows fluid to pass through and collect underneath the retina, which in turn pulls the retina away from its underlying tissues. The area with the tear loses blood supply, causing one to lose vision in the area. Rhegmatogenous: This type of detachment is the most common and is caused by a hole or tear in the retina. There are 3 main types of retinal detachment:
Eye disease or disorder like retinoschisis, uveitis or thinning of the peripheral retina (lattice degeneration). Ageing - people over the age of 50 have a higher risk of developing it. Risk-increasing Factors of Retinal Detachmentīelow are factors that increase the risk of developing a retinal detachment: Conditions such as injury, inflammatory disorders, tumours or age-related macular degeneration are the common causes of Exudative Detachment. Exudative: This type of detachment happens when fluid builds up behind the retina, but there is no retina damage - no holes or tears in the retina. People with poorly controlled diabetes or other conditions may be at risk or experience Tractional Detachment. Tractional: This type of detachment occurs when the retina pulls away from the back of the eye because of scar tissue growing on the retina’s surface. Rhegmatogenous is largely associated with ageing, but one can also have it due to an eye injury or severe nearsightedness. Also, if the vitreous - which is the gel-like material in the inside of your eye - passes through the tear to the space behind the retina, it might result in retinal detachment. The tear also allows fluid to pass through and collect underneath the retina, which in turn pulls the retina away from its underlying tissues. The area with the tear loses blood supply, causing one to lose vision in the area. Rhegmatogenous: This type of detachment is the most common and is caused by a hole or tear in the retina. There are 3 main types of retinal detachment: 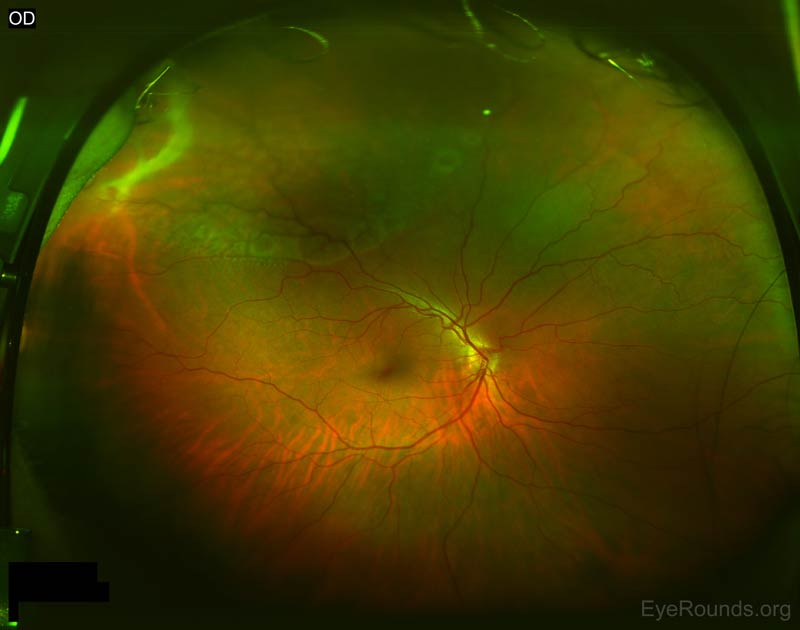

The most common causes of a detached retina are ageing and eye injury. A “curtain” of darkness over your vision.Sudden floaters (small flecks or threads in your vision) or flashes of light.Risk-increasing Factors of Retinal Detachment.Thirthahalli’s Multi-Specialty Eye Clinic.Accommodative and Vergence Disorder Management.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
